03-spring-cloud-gateway-源码分析
- 它们存在一个共同问题:路由配置变更后必须重启Gateway应用才能生效。这实在是不适合生产环境!
- 所以我们要实现动态路由
了解原理最好的方法是读源码,因此我们可以从源码入手,了解它是如何工作的,这样知其所以然->知其如何然。可以不仅仅模仿网上的几种方法,还能实现其他的方法。 这篇文章和余下部分主要分析源码。
1.启动过程
首先观察配置类,配置类生效的步骤如下。
one=>start: GatewayLoadBalancerClientAutoConfiguration
two=>operation: GatewayClassPathWarningAutoConfiguratio
th=>operation: GatewayRedisAutoConfiguration
fo=>end: GatewayAutoConfiguration
one->two->th->foGatewayLoadBalancerClientAutoConfiguration
初始化ReactiveLoadBalancerClientFilter类
GatewayClassPathWarningAutoConfiguratio
用于检查项目是否正确导入 spring-boot-starter-webflux 依赖,而不是错误导入 spring-boot-starter-web 依赖。GatewayRedisAutoConfiguration
初始化 RedisRateLimiter
RequestRateLimiterGatewayFilterFactory 基于 RedisRateLimiter 实现网关的限流功能GatewayAutoConfiguration
Spring Cloud Gateway 核心配置类
初始化的bean如下- NettyConfiguration
- GlobalFilter
- FilteringWebHandler
- GatewayProperties
- PrefixPathGatewayFilterFactory
- RoutePredicateFactory
- RouteDefinitionLocator
- RouteLocator
- RoutePredicateHandlerMapping
- GatewayWebfluxEndpoint
- NettyConfiguration ,Netty 配置类。
- 创建一个类型为 java.util.Objects.Consumer 的 Bean 对象。该 Consumer 会将传入类型为 reactor.ipc.netty.options.HttpClientOptions.Builder 的参数 opts ,设置 opts 的 poolResources 属性。调用 PoolResources.elastic(“proxy”) 方法,创建 name 属性为 “proxy” 的 reactor.ipc.netty.resources.PoolResources 。其中 “proxy” 用于实际使用时,打印日志的标记。
- 创建一个类型为 reactor.ipc.netty.http.client.HttpClient 的 Bean 对象。该 HttpClient 使用 Netty 实现的 Client 。
- 使用 HttpClient Bean ,创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.NettyRoutingFilter 的 Bean 对象。 NettyRoutingFilter 的代码实现见后文。
- 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.NettyWriteResponseFilter 的 Bean 对象。 NettyWriteResponseFilter 的代码实现解析见后文。
- 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.client.ReactorNettyWebSocketClient 的 Bean 对象,用于下文 WebsocketRoutingFilter 的 Bean 对象创建。
GlobalFilter
- 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.RouteToRequestUrlFilter 的 Bean 对象。
- 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.ForwardRoutingFilter 的 Bean 对象。
- 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.web.reactive.socket.server.WebSocketService 的 Bean 对象。
- 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.WebsocketRoutingFilter 的 Bean 对象。
FilteringWebHandler
当所有 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.GlobalFilter 初始化完成时( 包括上面的 NettyRoutingFilter / NettyWriteResponseFilter ),创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.FilteringWebHandler 的 Bean 对象
GatewayProperties
创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayProperties 的 Bean 对象,用于加载配置文件配置的 RouteDefinition / FilterDefinition 。
PrefixPathGatewayFilterFactory
创建 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.factory 包下的 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.factory.GatewayFilterFactory 接口的实现们。
RoutePredicateFactory
创建 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate 包下的 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.RoutePredicateFactory 接口的实现们。
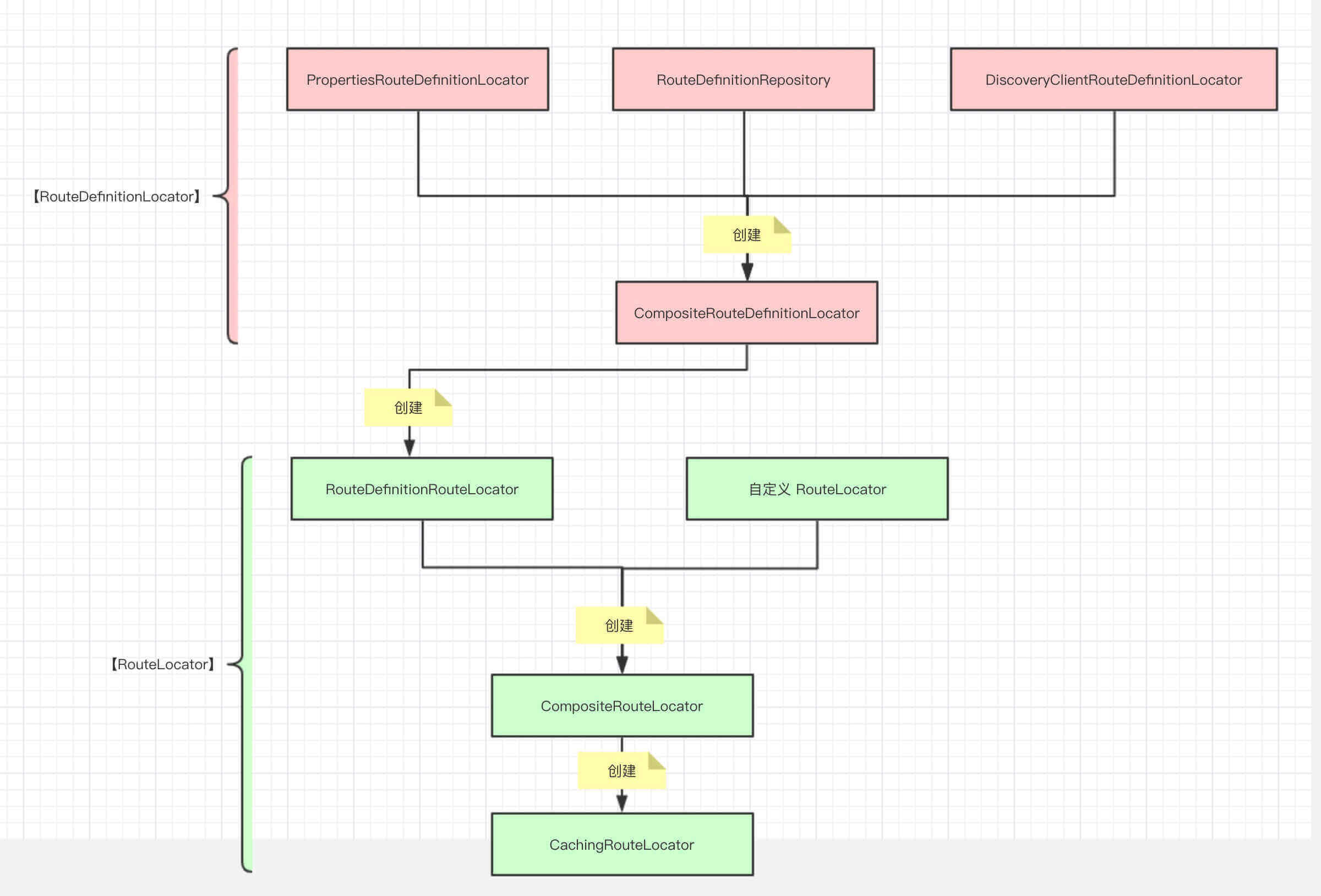
RouteDefinitionLocator (3.0.x 版本 改为直接注入下面几个对象)
- 使用 GatewayProperties Bean ,创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator 的 Bean 对象。
- 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository 的 Bean 对象。
- 使用上面创建的 RouteDefinitionLocator 的 Bean 对象们,创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.CompositeRouteDefinitionLocator 的 Bean 对象。
RouteLocator
- 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator 的 Bean 对象。
此处的 routeDefinitionLocator 参数,使用了 @Primary 注解的 CompositeRouteDefinitionLocator 的 Bean 对象。 - 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.CachingRouteLocator 的 Bean 对象。该 Bean 对象内嵌 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.CompositeRouteLocator 对象。
- 创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator 的 Bean 对象。
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping
创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 的 Bean 对象,用于查找匹配到 Route ,并进行处理。
GatewayWebfluxEndpoint
创建一个类型为 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.actuate.GatewayWebfluxEndpoint 的 Bean 对象,提供管理网关的 HTTP API .
2.核心组件和工作原理
2.1.基本组件
- Route
private final String id;
private final URI uri;
private final int order;
private final AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate;
private final List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters;
private final Map<String, Object> metadata;
- id,标识符,区别于其他 Route。
- destination uri,路由指向的目的地 uri,即客户端请求最终被转发的目的地。
- order,用于多个 Route 之间的排序,数值越小排序越靠前,匹配优先级越高。
- predicate,谓语,表示匹配该 Route 的前置条件,即满足相应的条件才会被路由到目的地 uri。
- gateway filters,过滤器用于处理切面逻辑,如路由转发前修改请求头等。
- AsyncPredicate
AsyncPredicate 定义了 4 种逻辑操作方法:public interface AsyncPredicate<T> extends Function<T, Publisher<Boolean>> { default AsyncPredicate<T> and(AsyncPredicate<? super T> other) { return new AndAsyncPredicate<>(this, other); } default AsyncPredicate<T> negate() { return new NegateAsyncPredicate<>(this); } default AsyncPredicate<T> not(AsyncPredicate<? super T> other) { return new NegateAsyncPredicate<>(other); } default AsyncPredicate<T> or(AsyncPredicate<? super T> other) { return new OrAsyncPredicate<>(this, other); } ... }
- and ,与操作,即两个 Predicate 组成一个,需要同时满足。
- negate,取反操作,即对 Predicate 匹配结果取反。
- or,或操作,即两个 Predicate 组成一个,只需满足其一。
- not和其他的不同
- GatewayFilter
public interface GatewayFilter extends ShortcutConfigurable {
/**
* Name key.
*/
String NAME_KEY = "name";
/**
* Value key.
*/
String VALUE_KEY = "value";
/**
* Process the Web request and (optionally) delegate to the next {@code WebFilter}
* through the given {@link GatewayFilterChain}.
* @param exchange the current server exchange
* @param chain provides a way to delegate to the next filter
* @return {@code Mono<Void>} to indicate when request processing is complete
*/
Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain);
}2.2 Route 构建的原理
外部化配置是如何工作的?
Spring boot 遵循规约大于配置的原则,starter 模块都有对应的以模块名称作前缀,以 “AutoConfiguration” 后缀的自动装配类。同样的还有以模块名前缀,以Properties后缀的配置类作为支持。
Gateway 模块自动装配类为 GatewayAutoConfiguration,对应的配置类为 GatewayProperties。
- GatewayProperties。
/** * List of Routes. */ @NotNull @Valid private List<RouteDefinition> routes = new ArrayList<>(); /** * List of filter definitions that are applied to every route. */ private List<FilterDefinition> defaultFilters = new ArrayList<>();
- 表明以 “spring.cloud.gateway” 前缀的 properties 会绑定 GatewayProperties。
- 用来对 Route 进行定义。
- 用于定义默认的 Filter 列表,默认的 Filter 会应用到每一个 Route 上,gateway 处理时会将其与 Route 中指定的 Filter 进行合并后并逐个执行。
- RouteDefinition
private String id; @NotEmpty @Valid private List<PredicateDefinition> predicates = new ArrayList<>(); @Valid private List<FilterDefinition> filters = new ArrayList<>(); @NotNull private URI uri; private Map<String, Object> metadata = new HashMap<>(); private int order = 0;
- 定义 Route 的 id,2.x默认使用 UUID。3.x默认为0
- 定义 Predicate。
- 定义 Filter。
- 定义目的地 URI。
- 定义 Route 的序号。
- FilterDefinition
@NotNull
private String name;
private Map<String, String> args = new LinkedHashMap<>();
public FilterDefinition() {
}- 定义了 Filter 的名称,符合特定的命名规范,为对应的工厂名前缀。
- 一个键值对参数用于构造 Filter 对象
- PredicateDefinition
@NotNull private String name; private Map<String, String> args = new LinkedHashMap<>(); public PredicateDefinition() { } public PredicateDefinition(String text) { int eqIdx = text.indexOf('='); if (eqIdx <= 0) { throw new ValidationException( "Unable to parse PredicateDefinition text '" + text + "'" + ", must be of the form name=value"); } setName(text.substring(0, eqIdx)); String[] args = tokenizeToStringArray(text.substring(eqIdx + 1), ","); for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) { this.args.put(NameUtils.generateName(i), args[i]); } }
- 定义了 Predicate 的名称,它们要符固定的命名规范,为对应的工厂名称。
- 一个 Map 类型的参数,构造 Predicate 使用到的键值对参数。
- RoutePredicateFactory
@FunctionalInterface // ①
public interface RoutePredicateFactory<C> extends ShortcutConfigurable,
Configurable<C> { // ④
Predicate<ServerWebExchange> apply(C config); // ②
default AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> applyAsync(C config) { // ③
return toAsyncPredicate(apply(config));
}
}
// RoutePredicateFactory 扩展了 Configurable
public interface Configurable<C> {
Class<C> getConfigClass(); // ⑤
C newConfig(); // ⑥
}- 声明它是一个函数接口。
- 核心方法,即函数接口的唯一抽象方法,用于生产 Predicate,接收一个范型参数 config。
- 对参数 config 应用工厂方法,并将返回结果 Predicate 包装成 AsyncPredicate。包装成 AsyncPredicate 是为了使用非阻塞模型。
- 扩展了 Configurable 接口,从命名上可以推断 Predicate 工厂是支持配置的。
- 获取配置类的类型,支持范型,具体的 config 类型由子类指定。
- 创建一个 config 实例,由具体的实现类来完成。
- GatewayFilterFactory
// useful for javadsl
default GatewayFilter apply(String routeId, Consumer<C> consumer) {
C config = newConfig();
consumer.accept(config);
return apply(routeId, config);
}
default GatewayFilter apply(Consumer<C> consumer) {
C config = newConfig();
consumer.accept(config);
return apply(config);
}- GatewayFilterFactory 职责就是生产 GatewayFilter。
- 同样继承了 ShortcutConfigurable 和 Configurable 接口,支持配置。
- 核心方法,用于生产 GatewayFilter,接收一个范型参数 config 。
2.3 Predicate 示例
主要是观察一个Predicate是如何被读取的。
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
discovery:
locator:
lowerCaseServiceId: true
enabled: true
routes:
- id: admin-api
uri: lb://rrs-admin-api
predicates:
- Path=/admin-api/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1那么生成的 PredicateDefinition 对象 toString() 方法返回结果
PredicateDefinition {
name=’Path’,
args={_genkey_0=/admin-api/**]}
}
- 生产谓语的工厂
public class PathRoutePredicateFactory extends AbstractRoutePredicateFactory<PathRoutePredicateFactory.Config> { private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(PathRoutePredicateFactory.class); private static final String MATCH_TRAILING_SLASH = "matchTrailingSlash"; private PathPatternParser pathPatternParser = new PathPatternParser(); public PathRoutePredicateFactory() { super(Config.class); } private static void traceMatch(String prefix, Object desired, Object actual, boolean match) { if (log.isTraceEnabled()) { String message = String.format("%s \"%s\" %s against value \"%s\"", prefix, desired, match ? "matches" : "does not match", actual); log.trace(message); } } public void setPathPatternParser(PathPatternParser pathPatternParser) { this.pathPatternParser = pathPatternParser; } @Override public List<String> shortcutFieldOrder() { return Arrays.asList("patterns", MATCH_TRAILING_SLASH); } @Override public ShortcutType shortcutType() { return ShortcutType.GATHER_LIST_TAIL_FLAG; } @Override public Predicate<ServerWebExchange> apply(Config config) { //1 final ArrayList<PathPattern> pathPatterns = new ArrayList<>(); synchronized (this.pathPatternParser) { pathPatternParser.setMatchOptionalTrailingSeparator(config.isMatchTrailingSlash()); config.getPatterns().forEach(pattern -> { PathPattern pathPattern = this.pathPatternParser.parse(pattern); pathPatterns.add(pathPattern); }); } return new GatewayPredicate() { @Override public boolean test(ServerWebExchange exchange) { PathContainer path = parsePath(exchange.getRequest().getURI().getRawPath()); PathPattern match = null; for (int i = 0; i < pathPatterns.size(); i++) { PathPattern pathPattern = pathPatterns.get(i); if (pathPattern.matches(path)) { match = pathPattern; break; } } if (match != null) { traceMatch("Pattern", match.getPatternString(), path, true); PathMatchInfo pathMatchInfo = match.matchAndExtract(path); putUriTemplateVariables(exchange, pathMatchInfo.getUriVariables()); exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_MATCHED_PATH_ATTR, match.getPatternString()); String routeId = (String) exchange.getAttributes().get(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_ROUTE_ATTR); if (routeId != null) { // populated in RoutePredicateHandlerMapping exchange.getAttributes().put(GATEWAY_PREDICATE_MATCHED_PATH_ROUTE_ID_ATTR, routeId); } return true; } else { traceMatch("Pattern", config.getPatterns(), path, false); return false; } } @Override public String toString() { return String.format("Paths: %s, match trailing slash: %b", config.getPatterns(), config.isMatchTrailingSlash()); } }; }
- 返回一个GatewayPredicate 对象,test方法返回true则通过,请求可以按这个规则走。
- PredicateDefinition 对象又是如何转换成 PathRoutePredicateFactory.Config 对象的?
- 这要涉及 RouteLocator 组件。
- RouteLocator
Route 的定位器或者说探测器,是用来获取 Route 信息的。
外部化配置定义 Route 使用的是 RouteDefinition 组件。同样的也有配套的 RouteDefinitionLocator 组件。
RouteLocator
public interface RouteLocator {
Flux<Route> getRoutes(); // ①
}RouteDefinitionLocator
public interface RouteDefinitionLocator {
Flux<RouteDefinition> getRouteDefinitions(); // ①
}- RouteDefinitionRouteLocator
RouteLocator 最主要的实现类,用于将 RouteDefinition 转换成 Route。public class RouteDefinitionRouteLocator implements RouteLocator { /** * Default filters name. */ public static final String DEFAULT_FILTERS = "defaultFilters"; protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); private final RouteDefinitionLocator routeDefinitionLocator; private final ConfigurationService configurationService; private final Map<String, RoutePredicateFactory> predicates = new LinkedHashMap<>(); private final Map<String, GatewayFilterFactory> gatewayFilterFactories = new HashMap<>(); private final GatewayProperties gatewayProperties; public RouteDefinitionRouteLocator(RouteDefinitionLocator routeDefinitionLocator, //1 List<RoutePredicateFactory> predicates, //2 List<GatewayFilterFactory> gatewayFilterFactories,//3 GatewayProperties gatewayProperties, //4 ConfigurationService configurationService) { //5 this.routeDefinitionLocator = routeDefinitionLocator; this.configurationService = configurationService; initFactories(predicates); gatewayFilterFactories.forEach(factory -> this.gatewayFilterFactories.put(factory.name(), factory)); this.gatewayProperties = gatewayProperties; } ... }- routeDefinitionLocator 用于加载外部配置的RouteDefinitionLocator类
- List
predicates 加载谓语的工厂集合 - gatewayFilterFactories ,加载过滤器的工厂集合
- GatewayProperties gatewayProperties ,外部化配置类。
- ConfigurationService configurationService ,是一个用来
该类依赖 GatewayProperties 对象,后者已经携带了 List 结构的 RouteDefinition,那为什么还要依赖 RouteDefinitionLocator 来提供 RouteDefinition?
- 这里并不会直接使用到 GatewayProperties 类中的 RouteDefinition,仅是用到其定义的 default filters,这会应用到每一个 Route 上。
- 最终传入的 RouteDefinitionLocator 实现上是 CompositeRouteDefinitionLocator 的实例,它组合了 GatewayProperties 中所定义的 routes。
在自动装配类中
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator propertiesRouteDefinitionLocator(GatewayProperties properties) {1
return new PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator(properties);//1
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(RouteDefinitionRepository.class)
public InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository inMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository() {
return new InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository();
}
@Bean
@Primary
public RouteDefinitionLocator routeDefinitionLocator(List<RouteDefinitionLocator> routeDefinitionLocators) {
return new CompositeRouteDefinitionLocator(Flux.fromIterable(routeDefinitionLocators));//2
}
- 是RouteDefinitionLocator 的实现类,RouteDefinition 信息来自 GatewayProperties。
- 使用 CompositeRouteDefinitionLocator 实现,它组合了多个 RouteDefinitionLocator 实例。这给用户(开发者)提供了可扩展的余地,用户可以根据需要扩展自己的 RouteDefinitionLocator,比如 RouteDefinition 可源自数据库。
比如 RouteDefinition 可源自数据库。
这里就可以实现动态路由
- 一种是主动触发,更新路由,路由可以在数据库中,也可以在各种缓存中,也可以在直接返回一个文本文件。
- 二是事件触发,例如当nacos配置更新,自动更新路由。甚至自己写事件,当数据库特定表更新则更新路由。
RouteDefinitionRouteLocator核心方法
@Override
public Flux<Route> getRoutes() {
Flux<Route> routes = this.routeDefinitionLocator.getRouteDefinitions().map(this::convertToRoute);//1
if (!gatewayProperties.isFailOnRouteDefinitionError()) {
// instead of letting error bubble up, continue
routes = routes.onErrorContinue((error, obj) -> {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("RouteDefinition id " + ((RouteDefinition) obj).getId()
+ " will be ignored. Definition has invalid configs, " + error.getMessage());
}
});
}
return routes.map(route -> {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("RouteDefinition matched: " + route.getId());
}
return route;
});
}
private Route convertToRoute(RouteDefinition routeDefinition) { //2
AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate = combinePredicates(routeDefinition);
List<GatewayFilter> gatewayFilters = getFilters(routeDefinition);//3
return Route.async(routeDefinition).asyncPredicate(predicate).replaceFilters(gatewayFilters).build();//4
}
- 调用 convertToRoute 方法将 RouteDefinition 转换成 Route。
- 将 PredicateDefinition 转换成 AsyncPredicate。
- 将 FilterDefinition 转换成 GatewayFilter。
- 根据 ② 和 ③ 两步骤定义的变量生成 Route 对象。
PredicateDefinition 转换成 AsyncPredicate
private AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> combinePredicates(RouteDefinition routeDefinition) { List<PredicateDefinition> predicates = routeDefinition.getPredicates(); if (predicates == null || predicates.isEmpty()) { // this is a very rare case, but possible, just match all return AsyncPredicate.from(exchange -> true); } AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> predicate = lookup(routeDefinition, predicates.get(0));//1 for (PredicateDefinition andPredicate : predicates.subList(1, predicates.size())) { AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> found = lookup(routeDefinition, andPredicate);//2 predicate = predicate.and(found);//3 } return predicate; }- 调用 lookup 方法,将列表中第一个 PredicateDefinition 转换成 AsyncPredicate。
- 循环调用,将列表中每一个 PredicateDefinition 都转换成 AsyncPredicate。
- 应用and操作,将所有的 AsyncPredicate 组合成一个 AsyncPredicate 对象。
PredicateDefinition 都转换成 AsyncPredicate。过程
private AsyncPredicate<ServerWebExchange> lookup(RouteDefinition route, PredicateDefinition predicate) { RoutePredicateFactory<Object> factory = this.predicates.get(predicate.getName());//1 if (factory == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to find RoutePredicateFactory with name " + predicate.getName()); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("RouteDefinition " + route.getId() + " applying " + predicate.getArgs() + " to " + predicate.getName()); } // @formatter:off Object config = this.configurationService.with(factory) .name(predicate.getName()) .properties(predicate.getArgs()) .eventFunction((bound, properties) -> new PredicateArgsEvent( RouteDefinitionRouteLocator.this, route.getId(), properties)) .bind();//2 // @formatter:on return factory.applyAsync(config);//3 }
这是3.0.x的代码,和2.0版本的有些不同,但大致上变化不大。
- 根据 predicate 名称获取对应的 predicate factory。
- 创建一个 config 类对象,产生的参数绑定到 config 对象上。
- 将 cofing 作参数代入,调用 factory 的 applyAsync 方法创建 AsyncPredicate 对象。
- FilterDefinition 转换成 GatewayFilter
private List<GatewayFilter> getFilters(RouteDefinition routeDefinition) {
List<GatewayFilter> filters = new ArrayList<>();
// TODO: support option to apply defaults after route specific filters?
if (!this.gatewayProperties.getDefaultFilters().isEmpty()) {
filters.addAll(loadGatewayFilters(routeDefinition.getId(),
new ArrayList<>(this.gatewayProperties.getDefaultFilters())));
}//1
if (!routeDefinition.getFilters().isEmpty()) {
filters.addAll(loadGatewayFilters(routeDefinition.getId(), new ArrayList<>(routeDefinition.getFilters())));
}//2
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(filters);//3
return filters;
}
/************************************************************/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<GatewayFilter> loadGatewayFilters(String id, List<FilterDefinition> filterDefinitions) {
ArrayList<GatewayFilter> ordered = new ArrayList<>(filterDefinitions.size());
for (int i = 0; i < filterDefinitions.size(); i++) {
FilterDefinition definition = filterDefinitions.get(i);
GatewayFilterFactory factory = this.gatewayFilterFactories.get(definition.getName());
if (factory == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Unable to find GatewayFilterFactory with name " + definition.getName());
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("RouteDefinition " + id + " applying filter " + definition.getArgs() + " to "
+ definition.getName());
}
// @formatter:off
Object configuration = this.configurationService.with(factory)
.name(definition.getName())
.properties(definition.getArgs())
.eventFunction((bound, properties) -> new FilterArgsEvent(
// TODO: why explicit cast needed or java compile fails
RouteDefinitionRouteLocator.this, id, (Map<String, Object>) properties))
.bind();
// @formatter:on
// some filters require routeId
// TODO: is there a better place to apply this?
if (configuration instanceof HasRouteId) {
HasRouteId hasRouteId = (HasRouteId) configuration;
hasRouteId.setRouteId(id);
}
GatewayFilter gatewayFilter = factory.apply(configuration);
if (gatewayFilter instanceof Ordered) {
ordered.add(gatewayFilter);
}
else {
ordered.add(new OrderedGatewayFilter(gatewayFilter, i + 1));
}
}
return ordered;
}
- 处理 GatewayProperties 中定义的默认的 FilterDefinition,转换成 GatewayFilter。
转换逻辑
- 根据 filter 名称获取对应的 filter factory。
- 创建一个 config 类对象,产生的参数绑定到 config 对象上。
- 将 cofing 作参数代入,调用 factory 的 applyAsync 方法创建 GatewayFilter 对象。
- 将 RouteDefinition 中定义的 FilterDefinition 转换成 GatewayFilter。
- 对 GatewayFilter 进行排序。
小结
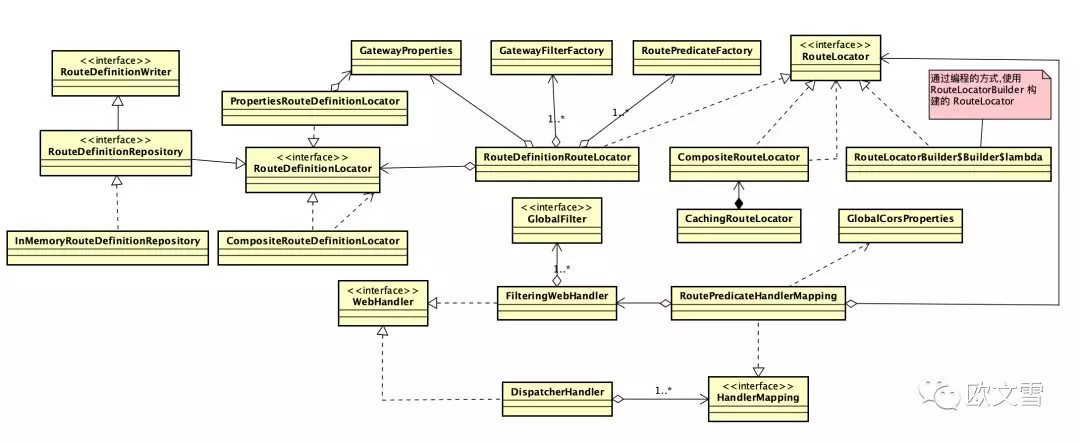
- RouteDefinitionRouteLocator 这是一个重要的中间类,用于将 RouteDefinition 转换成 Route。
- GatewayProperties,读取本地配置文件,并生成配置类。
- spring boot 项目中,有autoconfig 会有对应的 Properties类。
- RouteDefinitionLocator,这是一个加载路由基本信息的接口,有几个实现类。
- CachingRouteDefinitionLocator ,从缓存中获取路由定义。
- DiscoveryClientRouteDefinitionLocator,从注册中心获取路由定义。
- PropertiesRouteDefinitionLocator,从本地即GatewayProperties中获取路由定义。
- CompositeRouteDefinitionLocator,集合了其他几个RouteDefinitionLocator的路由定义。
- RouteLocator 是一个由RouteDefinitionLocator获取Route的接口。有以下几个实现类。
- CachingRouteLocator RoutePredicateHandlerMapping 使用 CachingRouteLocator 来获取 Route 信息。
- CompositeRouteLocator
- RouteDefinitionRouteLocator 就是最开始提到的类。
- RoutePredicateFactory,加载路由谓语的工厂,有很多实现类。RouteDefinitionRouteLocator使用不同的工厂,生成工厂对应的RoutePredicate。
- GatewayFilterFactory,加载过滤器的工厂。RouteDefinitionRouteLocator使用不同的工厂,生成对应的GatewayFilter。
- Route 目标路由对象,每个路由对象有谓语集合和过滤器集合,他们由RouteDefinitionRouteLocator对象中的方法,通过工厂类们转换RouteDefinition,将谓语和过滤器集合添加进去。
- RouteDefinitionRepository,是一个接口,继承RouteDefinitionLocator, RouteDefinitionWriter,常常用来实现动态路由。
- InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository 官方只有这一个实现类。