sc-gateway-11-异常处理
先上异常处理的步骤
1. 处理异常的步骤
- 抛出ResponseStatusException异常
第一种就是抛出 ResponseStatusException异常,如下图所示。
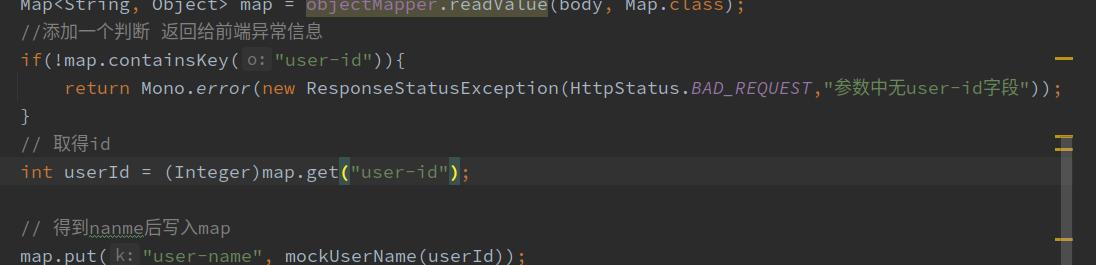
还需要在yml配置如下图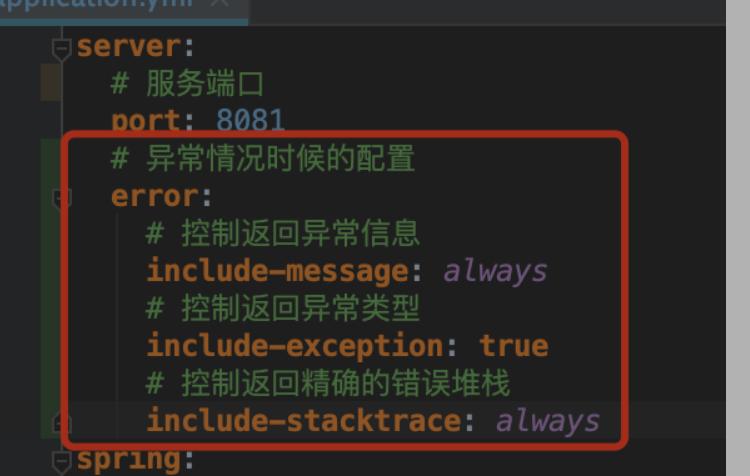
这是因为DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler.isIncludeMessage方法是这样的
protected boolean isIncludeMessage(ServerRequest request, MediaType produces) {
switch(this.errorProperties.getIncludeMessage()) {
case ALWAYS:
return true;
case ON_PARAM:
return this.isMessageEnabled(request);
default:
return false;
}
}会读取配置,然后按照配置文件的需求返回信息。
- 自定义异常,带ResponseStatus注解
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus;
@ResponseStatus(code= HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST,reason = "user-id不能为空")
public class TestGatewayException extends Exception{
}返回的时候返回这个异常类
2. 源码分析
spring-cloud-gateway 是基于spring-reactive技术的,没有使用servlet。spring-cloud-gateway 异常的处理也是由reactive的api完成的。
- 配置类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error 包下有一个类
ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,这个配置类注入了两个重要的类。
DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler:这个类是ErrorWebExceptionHandler的实现类
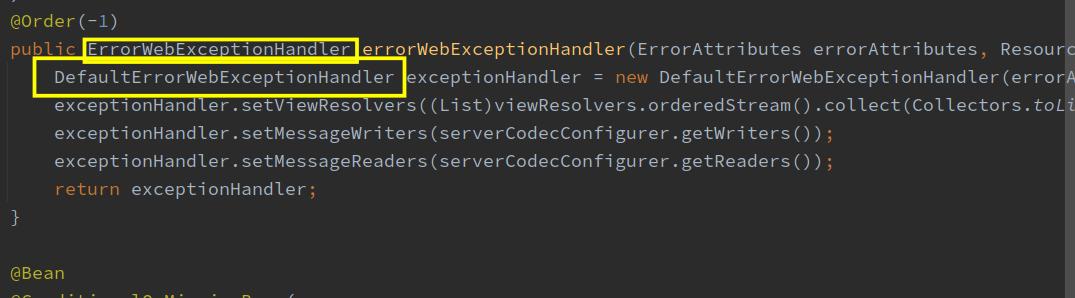
处理异常时,会通过FluxOnErrorResume调用到这个ErrorWebExceptionHandler的handle方法处理,该方法在其父类AbstractErrorWebExceptionHandler.java中,如下图,红框位置的代码是关键,异常返回内容就是在这里决定的:
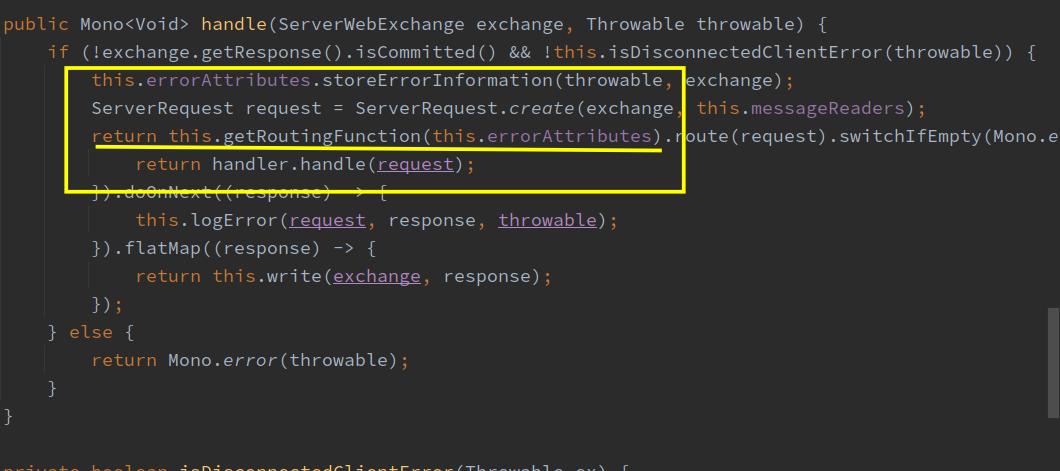
会发现此方法调用 DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler 中的方法 getRoutingFunctionprotected RouterFunction<ServerResponse> getRoutingFunction(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes) { return RouterFunctions.route(this.acceptsTextHtml(), this::renderErrorView).andRoute(RequestPredicates.all(), this::renderErrorResponse); } ``` this::renderErrorResponse如下所示 ```java protected Mono<ServerResponse> renderErrorResponse(ServerRequest request) { //构造返回的map对象 Map<String, Object> error = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL)); //返回信息 return ServerResponse.status(this.getHttpStatus(error)).contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).body(BodyInserters.fromValue(error)); }经过上述过程,可以知道。
返回给调用方的状态码,取决于getHttpStatus方法的返回值
返回给调用方的body,取决于error的内容protected int getHttpStatus(Map<String, Object> errorAttributes) { return (int) errorAttributes.get("status"); }可以发现 getErrorAttributes方法的返回值是决定返回码和返回body的关键!
public Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(ServerRequest request, ErrorAttributeOptions options) { Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = this.getErrorAttributes(request, options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)); if (!options.isIncluded(Include.EXCEPTION)) { errorAttributes.remove("exception"); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.STACK_TRACE)) { errorAttributes.remove("trace"); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.MESSAGE) && errorAttributes.get("message") != null) { errorAttributes.remove("message"); } if (!options.isIncluded(Include.BINDING_ERRORS)) { errorAttributes.remove("errors"); } return errorAttributes; } private Map<String, Object> getErrorAttributes(ServerRequest request, boolean includeStackTrace) { Map<String, Object> errorAttributes = new LinkedHashMap(); errorAttributes.put("timestamp", new Date()); errorAttributes.put("path", request.path()); Throwable error = this.getError(request); MergedAnnotation<ResponseStatus> responseStatusAnnotation = MergedAnnotations.from(error.getClass(), SearchStrategy.TYPE_HIERARCHY).get(ResponseStatus.class); HttpStatus errorStatus = this.determineHttpStatus(error, responseStatusAnnotation); //1 errorAttributes.put("status", errorStatus.value()); errorAttributes.put("error", errorStatus.getReasonPhrase()); errorAttributes.put("message", this.determineMessage(error, responseStatusAnnotation)); errorAttributes.put("requestId", request.exchange().getRequest().getId()); this.handleException(errorAttributes, this.determineException(error), includeStackTrace); return errorAttributes; } private HttpStatus determineHttpStatus(Throwable error, MergedAnnotation<ResponseStatus> responseStatusAnnotation) { // 异常对象是不是ResponseStatusException类型 // 如果是ResponseStatusException类型,就调用异常对象的getStatus方法作为返回值 // 如果异常对象既不是ResponseStatusException类型,也没有ResponseStatus注解,就返回500 return error instanceof ResponseStatusException ? ( (ResponseStatusException)error).getStatus() : (HttpStatus)responseStatusAnnotation.getValue("code", HttpStatus.class).orElse(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); } private String determineMessage(Throwable error, MergedAnnotation<ResponseStatus> responseStatusAnnotation) { if (error instanceof BindingResult) { // 异常对象是不是BindingResult类型 // 如果是,就用getMessage作为返回值 return error.getMessage(); } else if (error instanceof ResponseStatusException) { // 如果不是BindingResult类型,就看是不是ResponseStatusException类型 //// 如果是,就用getReason作为返回值 return ((ResponseStatusException)error).getReason(); } else { // 如果也不是ResponseStatusException类型, // 就看异常类有没有ResponseStatus注解,如果有就取该注解的reason属性作为返回值 String reason = (String)responseStatusAnnotation.getValue("reason", String.class).orElse(""); if (StringUtils.hasText(reason)) { return reason; } else { // 如果通过注解取得的reason也无效,就返回异常的getMessage字段 return error.getMessage() != null ? error.getMessage() : ""; } } }
- 查看上面的源码,返回码来自determineHttpStatus的返回,
message字段来自determineMessage的返回。 - 返回的逻辑就是我们在第一节中的处理逻辑
- 1 抛出一个ResponseStatusException异常
- 2 自定义异常,带ResponseStatus注解
3. 定制异常体的内容
在第一节我们已经可以返回想要的状态码和异常信息,但是请看下图。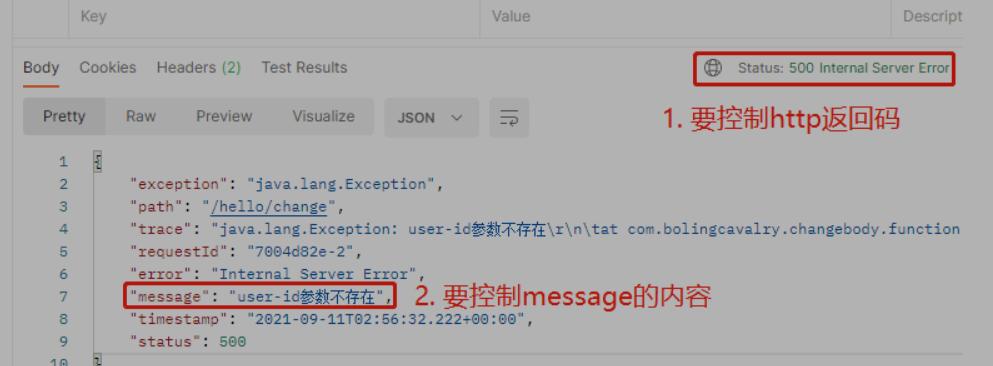
- 异常发生时系统固定返回8个字段,这就有些不够灵活了,在一些对格式和内容有严格要求的场景下,咱们需要能够完全控制返回码和返回body的内容,如下所示,只返回三个字段,每个字段都是完全为业务服务的
- 我们要通过编码定制异常发生时的返回信息,具体内容就只有code、message、data三个字段
具体该怎么做呢?
Spring Cloud Gateway是基于WebFlux的,咱们之前处理异常时用到的HttpServletRequest在Spring Cloud Gateway中并不适用,因此,不能用ControllerAdvice和ExceptionHandler的手段来处理全局异常
1 做个新的类继承DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler,覆盖其renderErrorResponse方法,新的renderErrorResponse方法中,按照实际业务需要来设置返回内容,没错,这就是咱们的思路,不过还要细化一下,最终具体的步骤如下:
- 新增一个异常类CustomizeInfoException.java,该类有三个字段:http返回码、业务返回码、业务描述信息
- 在返回异常的代码位置,使用CustomizeInfoException类来抛出异常,按照实际业务场景设置CustomizeInfoException实例的各个字段
- 新增MyErrorWebExceptionHandler.java,继承自DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler,重写了renderErrorResponse方法,这里面检查异常实例是否是CustomizeInfoException类型,如果是,就从其中取出http返回码、业务返回码、业务描述信息等字段,构造返回body的内容,异常实例若不是CustomizeInfoException类型,就保持之前的处理逻辑不变;
- 新增configuration类,用于将MyErrorWebExceptionHandler实例注册到spring环境
- 新增异常类CustomizeInfoException.java
@Data
public class CustomizeInfoException extends Exception {
/**
* http返回码
*/
private HttpStatus httpStatus;
/**
* body中的code字段(业务返回码)
*/
private String code;
/**
* body中的message字段(业务返回信息)
*/
private String message;
}- 修改RequestBodyRewrite.java的apply方法,这里面是在处理请求body,如果检查到没有user-id字段,就不将请求转发到服务提供方provider-hello,而是返回错误,这里的错误就用CustomizeInfoException类来处理:
// 如果请求参数中不含user-id,就返回异常
if (!map.containsKey("user-id")) {
CustomizeInfoException customizeInfoException = new CustomizeInfoException();
// 这里返回406,您可以按照业务需要自行调整
customizeInfoException.setHttpStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_ACCEPTABLE);
// 这里按照业务需要自行设置code
customizeInfoException.setCode("010020003");
// 这里按照业务需要自行设置返回的message
customizeInfoException.setMessage("请确保请求参数中的user-id字段是有效的");
return Mono.error(customizeInfoException);
}
- 异常处理类DemoErrorWebExceptionHandler.java
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ResourceProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.error.ErrorAttributes;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.BodyInserters;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.ServerRequest;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.ServerResponse;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CustomizeErrorWebExceptionHandler extends DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler {
public CustomizeErrorWebExceptionHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ResourceProperties resourceProperties, ErrorProperties errorProperties, ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
super(errorAttributes, resourceProperties, errorProperties, applicationContext);
}
@Override
protected Mono<ServerResponse> renderErrorResponse(ServerRequest request) {
// 返回码
int status;
// 最终是用responseBodyMap来生成响应body的
Map<String, Object> responseBodyMap = new HashMap<>();
// 这里和父类的做法一样,取得DefaultErrorAttributes整理出来的所有异常信息
Map<String, Object> error = getErrorAttributes(request, getErrorAttributeOptions(request, MediaType.ALL));
// 原始的异常信息可以用getError方法取得
Throwable throwable = getError(request);
// 如果异常类是咱们定制的,就定制
if (throwable instanceof CustomizeInfoException) {
CustomizeInfoException myGatewayException = (CustomizeInfoException) throwable;
// http返回码、body的code字段、body的message字段,这三个信息都从CustomizeInfoException实例中获取
status = myGatewayException.getHttpStatus().value();
responseBodyMap.put("code", myGatewayException.getCode());
responseBodyMap.put("message", myGatewayException.getMessage());
responseBodyMap.put("data", null);
} else {
// 如果不是咱们定制的异常,就维持和父类一样的逻辑
// 返回码
status = getHttpStatus(error);
// body内容
responseBodyMap.putAll(error);
}
return ServerResponse
// http返回码
.status(status)
// 类型和以前一样
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
// 响应body的内容
.body(BodyInserters.fromValue(responseBodyMap));
}
}- 配置类DemoErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration
import com.rrs.scgateway.exception.CustomizeErrorWebExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectProvider;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigureBefore;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ResourceProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.error.ErrorAttributes;
import org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.http.codec.ServerCodecConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.result.view.ViewResolver;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@AutoConfigureBefore(WebFluxAutoConfiguration.class)
public class CustomizeErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration {
private final ServerProperties serverProperties;
public CustomizeErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration(ServerProperties serverProperties) {
this.serverProperties = serverProperties;
}
//这里复制ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration 注入DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler
//的方法。然后改成返回CustomizeErrorWebExceptionHandler即可
//因为springboot版本的不同,代码会有改变,要跟着版本走。
@Bean
@Order(-1)
public ErrorWebExceptionHandler errorWebExceptionHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ResourceProperties resourceProperties, ObjectProvider<ViewResolver> viewResolvers, ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer, ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
CustomizeErrorWebExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = new CustomizeErrorWebExceptionHandler(errorAttributes, resourceProperties, this.serverProperties.getError(), applicationContext);
exceptionHandler.setViewResolvers((List)viewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
exceptionHandler.setMessageWriters(serverCodecConfigurer.getWriters());
exceptionHandler.setMessageReaders(serverCodecConfigurer.getReaders());
return exceptionHandler;
}
}- 为什么自定义的CustomizeErrorWebExceptionHandler类会生效呢?
- 因为原来的配置类中ConditionalOnMissingBean注解存在,所以我们自定义的注解生效后,这个DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler 会被自定义的替换掉。
一些逻辑也会走父类的逻辑,因为我们只重写了一个方法。@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean( value = {ErrorWebExceptionHandler.class}, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT ) @Order(-1) public ErrorWebExceptionHandler errorWebExceptionHandler(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ResourceProperties resourceProperties, ObjectProvider<ViewResolver> viewResolvers, ServerCodecConfigurer serverCodecConfigurer, ApplicationContext applicationContext) { DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = new DefaultErrorWebExceptionHandler(errorAttributes, resourceProperties, this.serverProperties.getError(), applicationContext); exceptionHandler.setViewResolvers((List)viewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList())); exceptionHandler.setMessageWriters(serverCodecConfigurer.getWriters()); exceptionHandler.setMessageReaders(serverCodecConfigurer.getReaders()); return exceptionHandler; }

