spring-oauth2-03-获取token的流程
1.获取token的流程
1.1 为什么要看流程
- 我们已经知道oauth2服务器的作用如左图所示
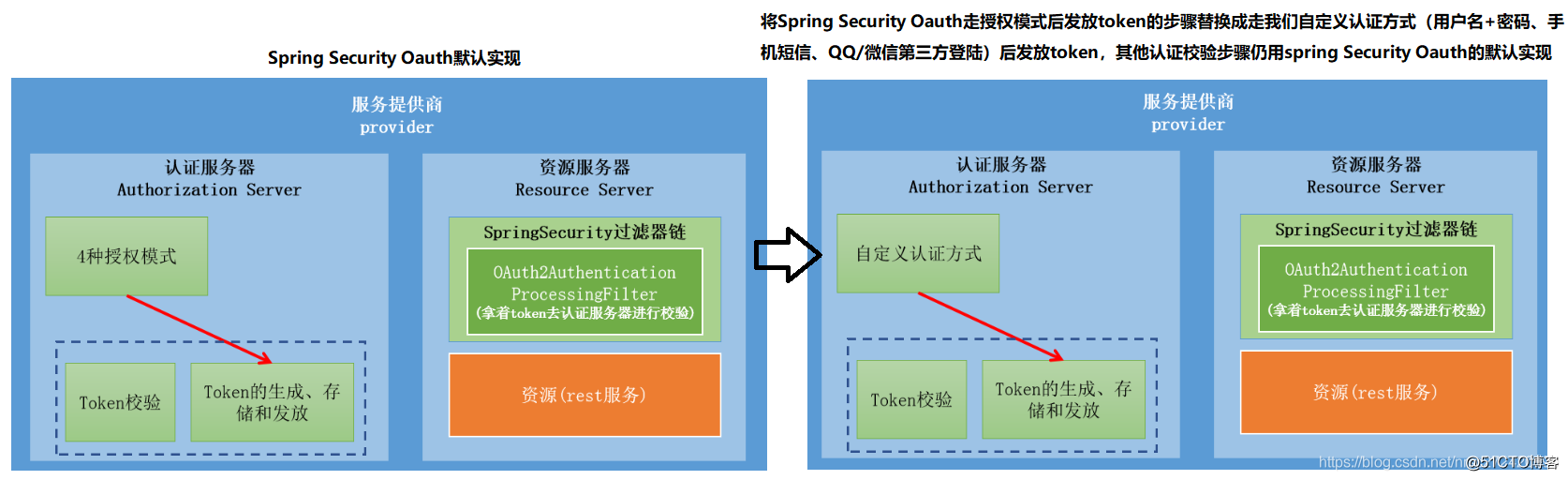
我们的目标就是将Spring Security OAuth默认的走授权流程后发放token的步骤替换成走我们自定义的认证方式后发放token,除此之外,其他的认证校验步骤(如访问资源服务器的认证、授权等)仍然可以使用Spring Security OAuth提供的默认实现来完成。
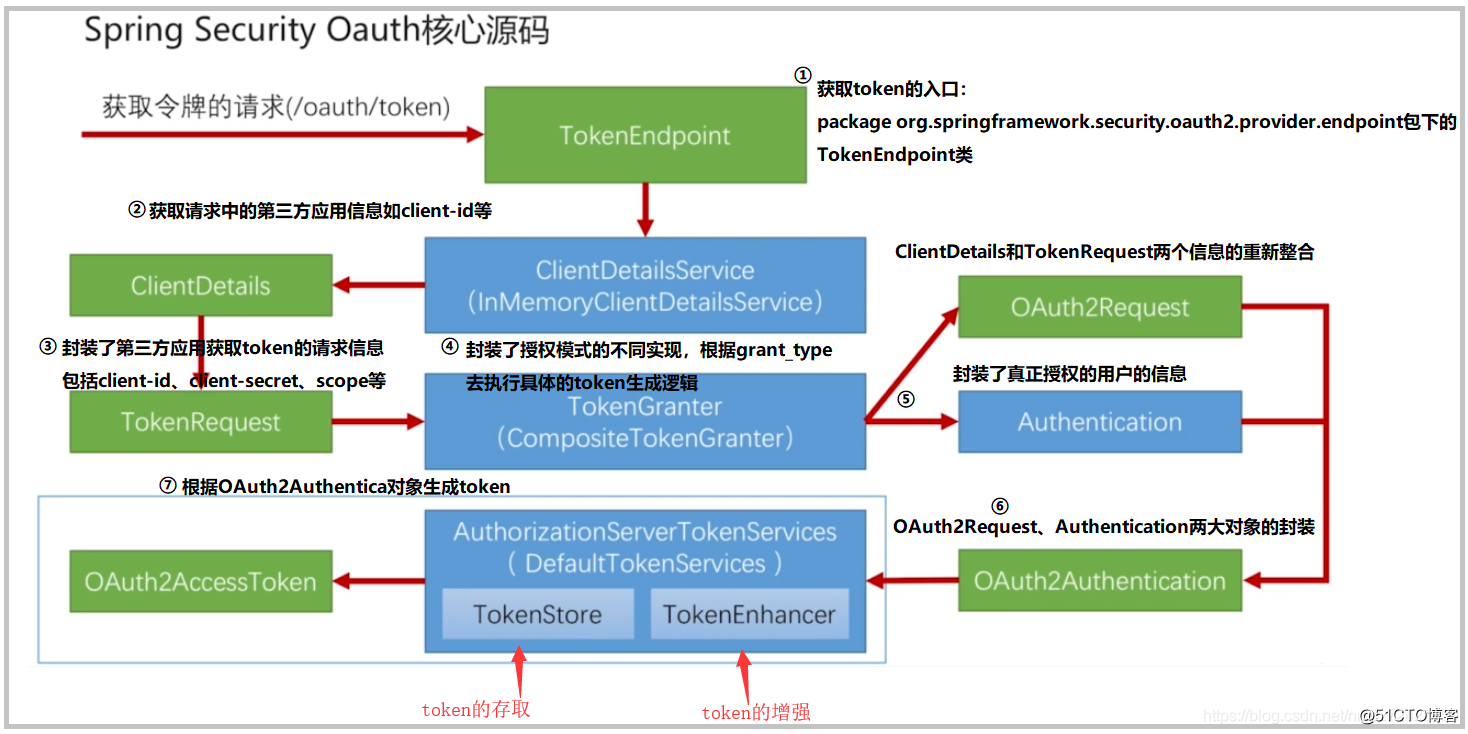
1.2 获取源码的核心流程
经过探究源码,先上结论,获取的核心流程如下
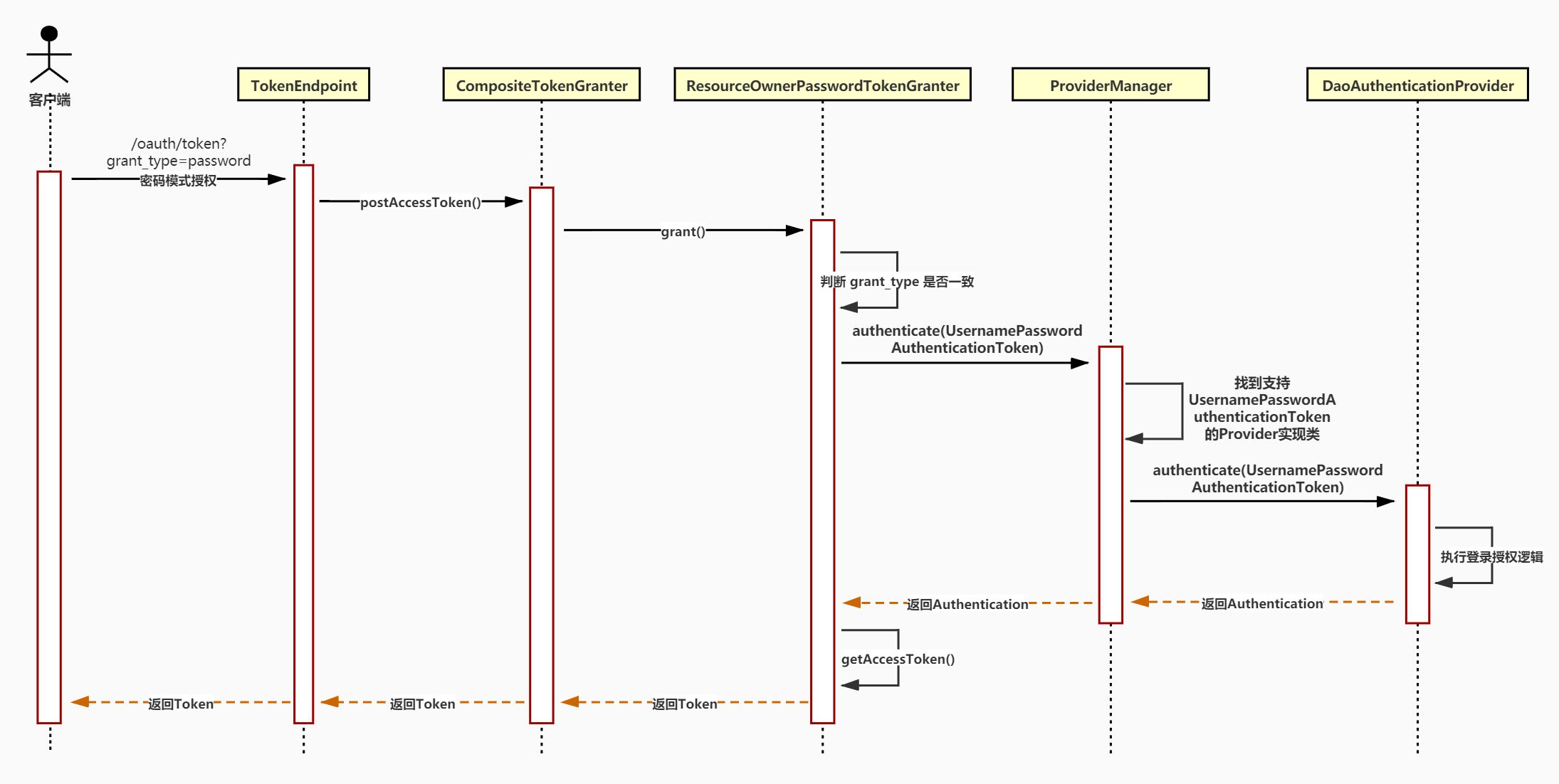
每一种授权方式有些差异,例如默认的密码授权时序图如下。
针对获取token的流程,我们探究查看代码。
1.3 源码简析
1 获取用户信息和认证用户
- 获取token的端点如下,发送获取token请求的源码会被解析到这里。
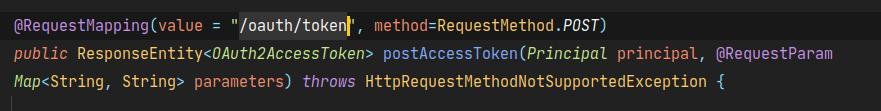
@RequestMapping(value = "/oauth/token", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<OAuth2AccessToken> postAccessToken(Principal principal, @RequestParam
Map<String, String> parameters) throws HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException {
if (!(principal instanceof Authentication)) {
throw new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
"There is no client authentication. Try adding an appropriate authentication filter.");
}
//获取客户端id
String clientId = getClientId(principal);
//从数据库获取客户端信息
ClientDetails authenticatedClient = getClientDetailsService().loadClientByClientId(clientId);
//构造TokenRequest对象 1
TokenRequest tokenRequest = getOAuth2RequestFactory().createTokenRequest(parameters, authenticatedClient);
if (clientId != null && !clientId.equals("")) {
// Only validate the client details if a client authenticated during this
// request.
if (!clientId.equals(tokenRequest.getClientId())) {
// double check to make sure that the client ID in the token request is the same as that in the
// authenticated client
throw new InvalidClientException("Given client ID does not match authenticated client");
}
}
if (authenticatedClient != null) {
oAuth2RequestValidator.validateScope(tokenRequest, authenticatedClient);
}
//没有授权方式就抛异常
if (!StringUtils.hasText(tokenRequest.getGrantType())) {
throw new InvalidRequestException("Missing grant type");
}
//隐士模式不需要走到这里面
if (tokenRequest.getGrantType().equals("implicit")) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Implicit grant type not supported from token endpoint");
}
//如果有scope参数,则置为空
if (isAuthCodeRequest(parameters)) {
// The scope was requested or determined during the authorization step
if (!tokenRequest.getScope().isEmpty()) {
logger.debug("Clearing scope of incoming token request");
tokenRequest.setScope(Collections.<String> emptySet());
}
}
//如果是刷新token 保持原有的scope
if (isRefreshTokenRequest(parameters)) {
// A refresh token has its own default scopes, so we should ignore any added by the factory here.
tokenRequest.setScope(OAuth2Utils.parseParameterList(parameters.get(OAuth2Utils.SCOPE)));
}
//获取token对象的真正的地方 2
OAuth2AccessToken token = getTokenGranter().grant(tokenRequest.getGrantType(), tokenRequest);
if (token == null) {
throw new UnsupportedGrantTypeException("Unsupported grant type");
}
return getResponse(token);
}- TokenRequest 对象如下
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class TokenRequest extends BaseRequest {
private String grantType;
....
}
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
abstract class BaseRequest implements Serializable {
private String clientId;
private Set<String> scope = new HashSet<String>();
private Map<String, String> requestParameters = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(new HashMap<String, String>());
....
}TokenRequest 请求中的参数做了封装,包括客户端id,授权方式,授权所用的其他参数等。
- getTokenGranter()会获取授权方式对应的TokenGranter,
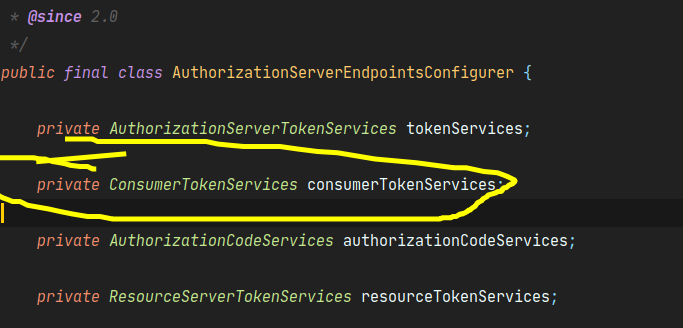
public class CompositeTokenGranter implements TokenGranter { private final List<TokenGranter> tokenGranters; public CompositeTokenGranter(List<TokenGranter> tokenGranters) { this.tokenGranters = new ArrayList<TokenGranter>(tokenGranters); } public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) { for (TokenGranter granter : tokenGranters) { //遍历授权器 调用授权器的方法获取token OAuth2AccessToken grant = granter.grant(grantType, tokenRequest); //1 if (grant!=null) { return grant; } } return null; } .... }
- grant()方法调用的是抽象类里的方法
public abstract class AbstractTokenGranter implements TokenGranter {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
private final AuthorizationServerTokenServices tokenServices;
public OAuth2AccessToken grant(String grantType, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
if (!this.grantType.equals(grantType)) {
return null;
}
String clientId = tokenRequest.getClientId();
ClientDetails client = clientDetailsService.loadClientByClientId(clientId);
validateGrantType(grantType, client);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Getting access token for: " + clientId);
}
return getAccessToken(client, tokenRequest);
}
protected OAuth2AccessToken getAccessToken(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
return tokenServices.createAccessToken(getOAuth2Authentication(client, tokenRequest)); //1
}
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request = requestFactory.createOAuth2Request(client, tokenRequest);
return new OAuth2Authentication(storedOAuth2Request, null);
}
.....
}- 我们以密码模式为例看授权器如何获取到token
密码模式对应的为ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter
上面的 getOAuth2Authentication(client, tokenRequest) 方法调用的是 ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter 实现类里面的方法。
public class ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter extends AbstractTokenGranter {
private static final String GRANT_TYPE = "password";
private final AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
public ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager,
AuthorizationServerTokenServices tokenServices, ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService, OAuth2RequestFactory requestFactory) {
this(authenticationManager, tokenServices, clientDetailsService, requestFactory, GRANT_TYPE);
}
protected ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager, AuthorizationServerTokenServices tokenServices,
ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService, OAuth2RequestFactory requestFactory, String grantType) {
super(tokenServices, clientDetailsService, requestFactory, grantType);
this.authenticationManager = authenticationManager;
}
@Override
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
Map<String, String> parameters = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(tokenRequest.getRequestParameters());
String username = parameters.get("username");
String password = parameters.get("password");
// Protect from downstream leaks of password
parameters.remove("password");
Authentication userAuth = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
((AbstractAuthenticationToken) userAuth).setDetails(parameters);
try {
userAuth = authenticationManager.authenticate(userAuth); // 1
}
catch (AccountStatusException ase) {
//covers expired, locked, disabled cases (mentioned in section 5.2, draft 31)
throw new InvalidGrantException(ase.getMessage());
}
catch (BadCredentialsException e) {
// If the username/password are wrong the spec says we should send 400/invalid grant
throw new InvalidGrantException(e.getMessage());
}
if (userAuth == null || !userAuth.isAuthenticated()) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Could not authenticate user: " + username);
}
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request = getRequestFactory().createOAuth2Request(client, tokenRequest);
return new OAuth2Authentication(storedOAuth2Request, userAuth);//2
}
}比较重要的是注释1
会通过authenticationManager的实现类ProviderManager来验证传入的信息。
ProviderManager维护AuthenticationProvide集合,遍历AuthenticationProvide集合,如果哪一个支持,则使用这个AuthenticationProvide实现类。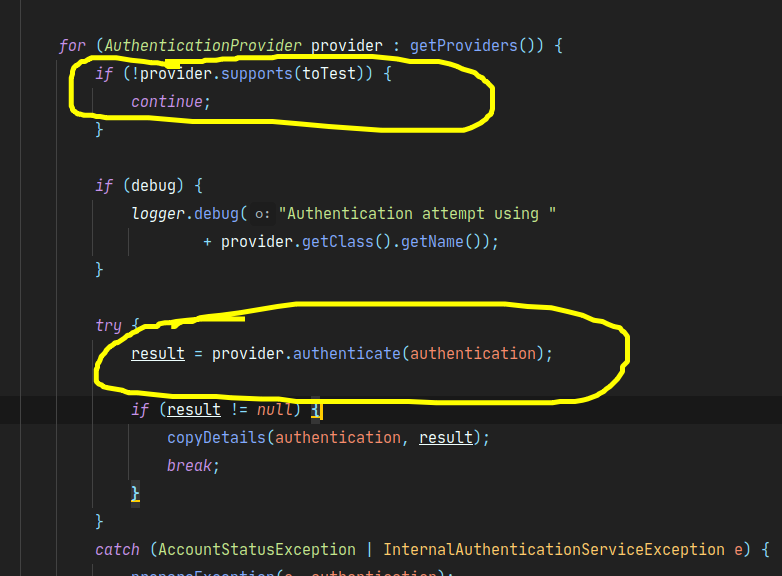
密码模式对应的AuthenticationProvide实现类就是 DaoAuthenticationProvider
public class DaoAuthenticationProvider extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider {
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username,
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
prepareTimingAttackProtection();
try {
UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username);
if (loadedUser == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(
"UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation");
}
return loadedUser;
}
catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) {
mitigateAgainstTimingAttack(authentication);
throw ex;
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException(ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
......
}
public abstract class AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider implements
AuthenticationProvider, InitializingBean, MessageSourceAware {
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) //2
throws AuthenticationException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication,
() -> messages.getMessage(
"AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports",
"Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported"));
// Determine username
String username = (authentication.getPrincipal() == null) ? "NONE_PROVIDED"
: authentication.getName();
boolean cacheWasUsed = true;
UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username);
if (user == null) {
cacheWasUsed = false;
try {
user = retrieveUser(username,
(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication); //1
}
.......
}
```
在AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider的authenticate方法 返回的userAuth是一个Authentication对象(具体是那个实现类不同授权模式不同)。
最终在ResourceOwnerPasswordTokenGranter中返回一个OAuth2Authentication对象,这是tokenrequest对象和Authentication对象的封装。
----------------------------
>小结
**源码读到现在,可以知晓它做的事情是。**
1. 我们拿到传递来的用户信息。
2. 根据信息里的授权模式找到了对应的授权类。
3. 对应的授权类又找到对应的认证类提供商进行了认证。
4. 使用传递过来的用户信息和认证得到的用户信息,得到OAuth2Authentication对象。
##### 2. 生成token
那么接下来就是拿着这个对象去生成token对象了

tokenServices官方暂时只有一个实现类DefaultTokenServices

DefaultTokenServices调用tokenstore获取token。
官方实现的tokenStore
- RedisTokenStore
- InMemoryTokenStore
- JdbcTokenStore
- JwtTokenStore
每一种tokenStore,实现的细节都不同。
要使用什么tokenStore自己可以使用第二篇将的配置授权服务器配置。
我们以RedisTokenStore为例探究

- 根据传入的OAuth2Authentication 生成一个key,猜测这个key应当和用户信息有关。
- 如果redis中没有这个key,那么accesstoken为null。返回null.
- 如果有,则说明已经登陆,则更新。//2
如果为null 返回上一层方法。

- 创建accesstoken
- 存储token
- 存储刷新token
--------------------------------
>小结
**生成token的过过程如下**
1. 获取TokenServices
2. TokenServices调用配置的 TokenStore 获取token
### 2. 修改
我们要修改框架,让他可以做微服务的授权中心。
#### 1.生成token的简化流程
>整体的生成token的过程可以梳理一下
> 1. 获取处理传入的信息
> 2. 获取授权类 (根据传入的授权模式)
> 3. 进行用户认证(根据授权类掉用时传入的对象,委托模式)
> 4. 认证通过一个对象
> 5. 获取TokenService
> 6. 使用TokenStore 获取token(配置)
改造
1. 一是增加授权模式
2. 增加认证模式
3. 增加tokenStore ,例如增加mogodb等存储方式,生成方法等。
4. TokenService 方法增强
授权模式和认证模式是一对一的
#### 增加一种授权模式
以增加手机号验证码为例子
1. 首先增加一个TokenGranter
```java
public class MobileSMSGranter extends AbstractTokenGranter {
private static final String GRANT_TYPE = "mobile_sms";
private final AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
public MobileSMSGranter(AuthenticationManager authenticationManager, AuthorizationServerTokenServices tokenServices
, ClientDetailsService clientDetailsService, OAuth2RequestFactory requestFactory) {
super(tokenServices, clientDetailsService, requestFactory, GRANT_TYPE);
this.authenticationManager = authenticationManager;
}
@Override
protected OAuth2Authentication getOAuth2Authentication(ClientDetails client, TokenRequest tokenRequest) {
Map<String, String> parameters = new LinkedHashMap<>(tokenRequest.getRequestParameters());
String mobile = parameters.get("mobile");
String sms = parameters.get("sms");
// Protect from downstream leaks of sms
parameters.remove("sms");
Authentication userAuth = new MobileSMSAuthenticationToken(mobile, sms); //1
((AbstractAuthenticationToken) userAuth).setDetails(parameters); //2
userAuth = authenticationManager.authenticate(userAuth);
if (userAuth == null || !userAuth.isAuthenticated()) {
throw new InvalidGrantException("Could not authenticate mobile: " + mobile);
}
OAuth2Request storedOAuth2Request = getRequestFactory().createOAuth2Request(client, tokenRequest);
return new OAuth2Authentication(storedOAuth2Request, userAuth);
}
}
注意注释1处,要根据这个类判断调用哪种认证器。
- 增加AbstractAuthenticationToken实现类
基本上和UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 这个官方实现类一样。
public class MobileSMSAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private static final long serialVersionUID = SpringSecurityCoreVersion.SERIAL_VERSION_UID;
// ~ Instance fields
// ================================================================================================
private final Object principal;
private Object credentials;
// ~ Constructors
// ===================================================================================================
/**
* This constructor can be safely used by any code that wishes to create a
* <code>UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken</code>, as the {@link #isAuthenticated()}
* will return <code>false</code>.
*
*/
public MobileSMSAuthenticationToken(String mobile, String password) {
super(null);
this.principal = mobile;
this.credentials = password;
setAuthenticated(false);
}
/**
* This constructor should only be used by <code>AuthenticationManager</code> or
* <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> implementations that are satisfied with
* producing a trusted (i.e. {@link #isAuthenticated()} = <code>true</code>)
* authentication token.
*
* @param principal
* @param authorities
*/
public MobileSMSAuthenticationToken(Object principal, Object credentials,
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
super.setAuthenticated(true);
}
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
@Override
public Object getCredentials() {
return this.credentials;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return this.principal;
}
@Override
public void setAuthenticated(boolean isAuthenticated) {
if (isAuthenticated) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot set this token to trusted - use constructor which takes a GrantedAuthority list instead");
}
super.setAuthenticated(false);
}
@Override
public void eraseCredentials() {
super.eraseCredentials();
}
}- 增加一个认证处理器
public class MobileSMSAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
private UserDetailServiceFactory userDetailsServiceFactory;
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
//发送消息服务 用于验证验证码
private MessageFeign messageFeign;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) {
MobileSMSAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = (MobileSMSAuthenticationToken) authentication;
String mobile = (String) authenticationToken.getPrincipal();
String sms = (String) authenticationToken.getCredentials();
//加载用户信息
UserDetails user = userDetailsServiceFactory.getService(authenticationToken).loadUserByMobile(mobile);
if (user == null) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("手机号错误");
}
//调用信息接口获取电话号码对应的验证码
Result<Boolean> booleanResult = messageFeign.smsCodeValid(mobile, SmsCodeTemplateEnums.ADMIN_SEND.getTemplateCode(), sms, false);
Boolean data = booleanResult.getData();
if (!data) {
throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException("验证码错误");
}
MobileSMSAuthenticationToken authenticationResult = new MobileSMSAuthenticationToken(user, sms, user.getAuthorities());
authenticationResult.setDetails(authenticationToken.getDetails());
return authenticationResult;
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return MobileSMSAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication);
}
}将这个类配置进框架
@Component public class MobileSMSAuthenticationSecurityConfig extends SecurityConfigurerAdapter<DefaultSecurityFilterChain, HttpSecurity> { @Resource private UserDetailServiceFactory userDetailsServiceFactory; @Autowired private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; //发送消息服务 用于验证验证码 @Autowired private MessageFeign messageFeign; @Override public void configure(HttpSecurity http) { //mobile provider MobileSMSAuthenticationProvider provider = new MobileSMSAuthenticationProvider(); provider.setUserDetailsServiceFactory(userDetailsServiceFactory); provider.setPasswordEncoder(passwordEncoder); provider.setMessageFeign(messageFeign); http.authenticationProvider(provider); } }要将这个TokenGranter 配置进框架
自定义bean list,然后配置进授权配置类。
@Bean
public TokenGranter tokenGranter() {}
配置类中配置
/**
* 配置身份认证器,配置认证方式,TokenStore,TokenGranter,OAuth2RequestFactory
* @param endpoints
*/
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) {
endpoints.tokenStore(tokenStore)
.authenticationManager(authenticationManager)
//.userDetailsService(userDetailsServiceFactory.getService(SecurityConstants.DEF_ACCOUNT_TYPE))
.authorizationCodeServices(authorizationCodeServices)
.exceptionTranslator(webResponseExceptionTranslator)
.tokenGranter(tokenGranter);
}
- 认证方式增加到框架
在SecurityConfig 配置类中添加。@Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.authorizeRequests() .anyRequest() //授权服务器关闭basic认证 .permitAll() .and() .logout() .logoutUrl(SecurityConstants.LOGOUT_URL) .logoutSuccessHandler(new OauthLogoutSuccessHandler()) .addLogoutHandler(oauthLogoutHandler) .clearAuthentication(true) .and() .apply(openIdAuthenticationSecurityConfig) .and() .apply(mobileAuthenticationSecurityConfig) .and() .apply(mobileSMSAuthenticationSecurityConfig) .and() .addFilterBefore(new LoginProcessSetTenantFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class) .csrf().disable() // 解决不允许显示在iframe的问题 .headers().frameOptions().disable().cacheControl();
增强redis
其他修改的方法
todo

